Colloidal Nanostructures
Introduction
In recent years, semiconductor colloidal nanostructures have attracted much attention due to their importance in fundamental research on low dimensional structures and great potential in a variety of applications, such as quantum information, light emitting diodes, spintronics and bio-labeling.
“Wet” chemical synthesis allows for great quantum efficiency and precise control of optical properties of produced colloidal nanostructures (via control of their size, shape and the surface conditions), while keeping low manufacturing costs.
Our research group mainly focuses on the exploration of the fine structure of band edge excitons and spin relaxation mechanisms in colloidal nanostructures using various magneto-optical spectroscopic techniques. The objects of our current research include core-shell colloidal nanocrystals, dot-in-rod structures (quantum rods), dot-in-plate structures and nanoplatelets.

Experimental Setup
Setup 1
Setup 1 (see figure below) is used to perform the magneto-PL and polarization-resolved PL decay measurement. The sample is mounted in Faraday geometry on a fiber-coupled holder inserted in a cryostat equipped with a 17 T magnet. The sample was excited through an optical fiber by a continuous wave diode laser for magneto-PL measurement or by a pico-second pulsed diode for PL decay measurement. The PL, collected through another multimode optical fiber, was either sent to a spectrometer and recorded by a CCD or a single photon-counting avalanche photodiode. A circular polarizer inserted between the sample and the detection fiber allowed to measure σ+ (σ-) polarized PL. The PL decay measurements were performed with a conventional time correlated single photon counting setup (instrumental response function ~800ps FWHM). The measurement with magnetic field can be performed from 2.2 K to 30 K. The measurement without magnetic field can be performed from 2.2 K up to room temperature.
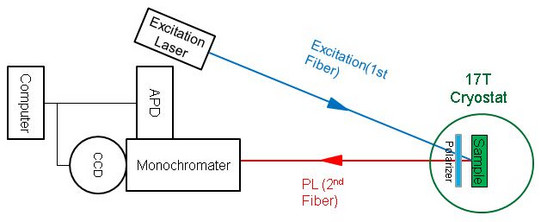
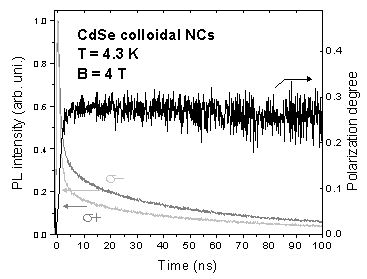
The figure below is an example of experimental result. This figure shows the PL decay of σ+ and σ- components from CdSe/CdS colloidal nanocrystals and time-resolved circular polarization degree. The rise time of the time-resolved polarization degree reflects the spin-flip time of carriers. Based on this result, the exciton lifetime, circular polarization degree, spin-flip rate of carriers at different magnetic field and temperature can be evaluated. Additionally, exciton or electron g-factor can be extracted by fitting the magnetic field dependence of the circular polarization degree.
Setup 2
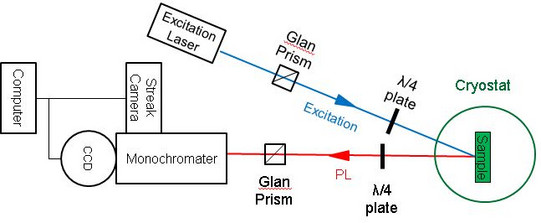
Setup 2 is used to perform fluorescence line narrowing measurement. As shown in the schematic below, the sample is mounted in a 10 T optical cryostat and excited resonantly with circularly polarized laser beam. The PL is send into a three-stage monochromater and recorded by a CCD. The λ/4 plate and Glan prism inserted in the detection path are used to select the σ+ or σ- polarized light. The temperature range of the cryostat is from 1.5 K to room temperature.
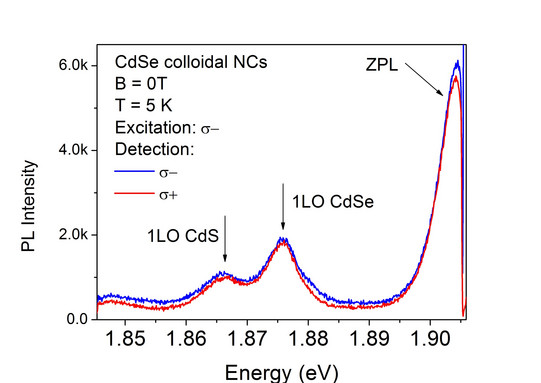
The following figures shows the spectra of an ensemble of CdSe colloidal NCs measured on setup 2. The advantage of the fluorescence line narrowing technique is that only NCs with very similar size can be excited. So compared with nonresonant excitation, the PL line is much narrower and the LP phonon lines can be clearly resolved.
Setup 3
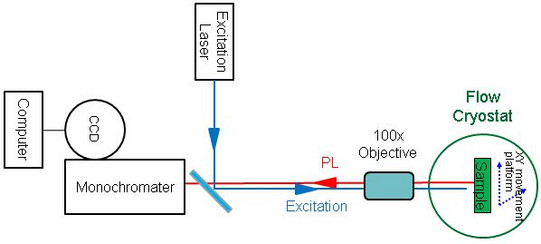
Setup 3 (see figure below) is used to perform single-nanoparticle PL spectroscopy of the studied objects. Sample is prepared by deposition of strongly diluted solution of colloidal nanoparticles onto a substrate (usually glass). The substrate is subsequently attached to the holder situated on a piezoelectric XY-movement platform inside a flow-cryostat. While the optical system remains unchanged, this platform facilitates scanning of the sample surface in search of single dots. The optical system is assembled in confocal configuration: a dichromatic mirror is used as a beam-splitter, thus allowing the excitation laser beam and the detected PL to travel along the same optical axis. To focus the excitation and to collect PL from the smallest possible area (thus measuring just a single particle), a 100x optical objective is used.
Experimental Techniques
- Polarization-resolved PL decay technique with the magnetic field up to 17 T
- Fluorescence line narrowing (FLN) technique
- Single-nanoparticle spectroscopy
Material system
We focus on II-VI semiconductor-based colloidal nanostructures including CdSe/CdS (core/shell), CdSe/CdS dot-in-plate structures, CdSe nanoplatelets and CdTe colloidal nanocrystals.
Objects
The objective of our reasearch is to understand the basic optical properities and spin dynamics of various colloidal nanocrystals.
Main Results
Results of investigation of magneto-optic properties of CdSe/CdS (core/shell) colloidal quantum dots and quantum rods as well as CdSe nanoplatelets are currntly being examined and are in the process of preparation for publication.
Current Offers For Bachelor-, Master- or PhD-Theses
Offers will be made on request. Usually there is always a topic available.
Contact
- Dr. Elena Shornikova
- Gang Qiang
Collaborations
- Universiteit Gent, Belgium
- Universiteit Utrecht, Netherlands
- IBM Research GmbH, Switzerland
- Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium
- Laboratoire Photons Et Matière, CNRS UPR5, Paris, France



